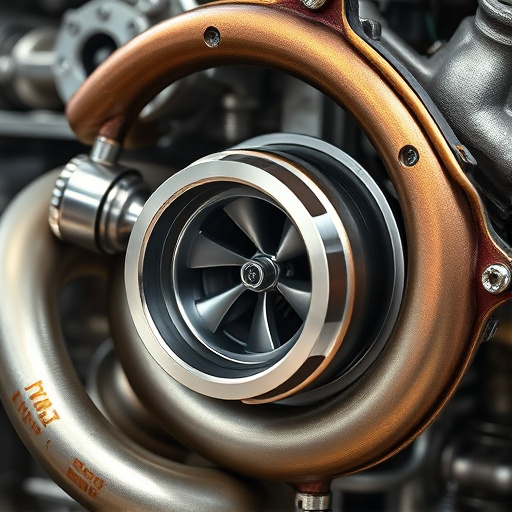
A turbo heat shield protects engines and intake systems from heat damage, ensuring cool air for optimal combustion. Strategically placed near the airbox, it prevents heat soak, boosting engine power in turbocharged vehicles. Optimizing intake location with a heat shield improves airflow, reducing pressure loss and maximizing cold, dense air flow for better performance.
A turbo heat shield is a crucial component in high-performance vehicles, acting as a protective barrier against intense heat generated by the turbocharger. This article delves into the fundamental principles of turbo heat shields and explores their significant impact on engine performance. We examine how these shields affect airbox placement, enhancing efficiency, and discuss optimizing intake location for maximum gain. By understanding these aspects, car enthusiasts can unlock improved engine response and overall vehicle dynamics.
- Understanding Turbo Heat Shield Basics
- Impact on Airbox: Benefits and Placement
- Optimizing Intake Location for Enhanced Performance
Understanding Turbo Heat Shield Basics

A turbo heat shield is a crucial component designed to protect both the engine and surrounding components from excessive heat generated by the turbine side of a turbocharger. This shield acts as a barrier, deflecting hot gases away from the intake airbox and other sensitive parts, such as sensors and electronic modules. By understanding the basics of how a turbo heat shield functions, automotive enthusiasts and mechanics can better appreciate its role in optimizing engine performance and ensuring longevity.
The primary purpose of a turbo heat shield is to insulate and shield the vulnerable areas of an automobile’s intake system. It does so by capturing and redirecting the intense heat produced during the turbocharger’s operation, particularly when dealing with high-performance exhaust systems or cat back exhaust configurations. This is especially important as these hot gases can cause damage to various components, leading to potential issues with engine performance and efficiency. Effective heat shielding ensures that the intake air remains cool, allowing for better combustion and overall engine health, even under extreme conditions.
Impact on Airbox: Benefits and Placement

The placement and design of a turbo heat shield can significantly impact the performance and efficiency of an engine’s air intake system. By strategically positioning this component, it becomes a powerful tool to enhance the overall capabilities of the vehicle. One of its key benefits is temperature regulation within the airbox. The heat shield acts as a barrier, preventing excessive heat from the exhaust system from reaching the air intake, which could otherwise dilute the charge air and reduce engine power. This results in a cooler, denser air supply, leading to improved combustion and increased horsepower, especially in turbocharged engines.
When it comes to placement, the turbo heat shield is typically designed to be mounted near or around the airbox and intake manifold. This strategic positioning ensures efficient heat dissipation and prevents heat soak, which can negatively affect engine performance. Many enthusiasts also choose to incorporate a cat back exhaust system alongside this modification, as it further reduces heat transfer into the intake. Additionally, some performance-oriented individuals may opt for suspension kits or performance exhaust upgrades, but these are not directly related to the turbo heat shield’s primary function.
Optimizing Intake Location for Enhanced Performance

Optimizing the intake location is a key aspect of enhancing engine performance, especially when incorporating a turbo heat shield into an vehicle’s design. This strategic adjustment allows for improved airflow, which is fundamental to the efficient operation of both the airbox and intake systems. By carefully positioning the air intake closer to the engine, you reduce the distance that air needs to travel, minimizing pressure loss and maximizing the flow of cold, dense air—a crucial element in fueling efficient combustion.
The turbo heat shield plays a significant role in this optimization process by managing the heat generated during the compression cycle, allowing for cooler intake air. This is particularly important for high-performance vehicles where peak engine power is achieved at higher RPMs. Cooler air intakes result in denser air, leading to improved horsepower and torque outputs. Additionally, strategically placing the airbox closer to the engine can help isolate it from unwanted vibrations and noise from suspension components, ensuring smoother operation of the entire air intake system and enhancing overall vehicle performance.
A turbo heat shield is not just a component; it’s a key enabler for optimal engine performance. By understanding its impact on both airbox positioning and intake location, car enthusiasts can unlock significant enhancements in their vehicle’s efficiency and power output. Incorporating a well-designed turbo heat shield offers a simple yet effective way to navigate the intricate relationship between cooling, airflow, and engine health, ultimately contributing to a smoother, more powerful driving experience.