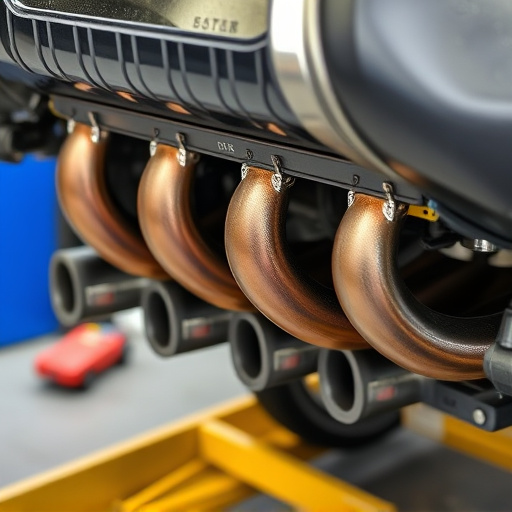
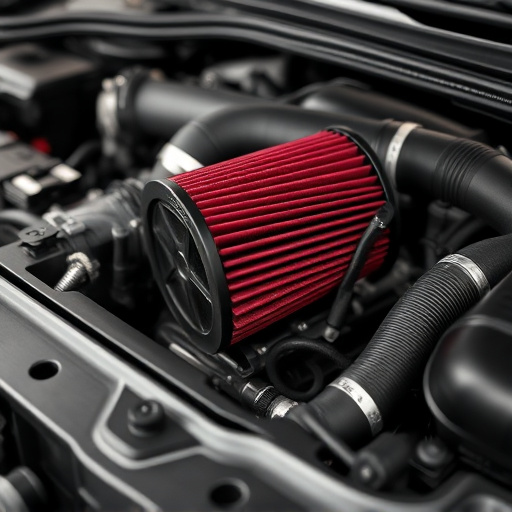
A turbo heat shield is a specialized component that insulates intake air from turbine-generated heat in turbocharged vehicles, maintaining cool IAT for optimal engine performance and efficiency. By preventing thermal transfer, it facilitates better compression ratios and efficient combustion, enhancing horsepower and torque across RPM ranges. This game-changer in automotive engineering protects critical intake components, allowing fine-tuning of air intake systems and integration of suspension kits for increased performance and stability.
Discover how turbo heat shields, an innovative automotive component, are revolutionizing engine performance. This article delves into the science behind these shields, their critical role in maintaining optimal intake air temperature, and their far-reaching benefits across various automotive applications. Understanding turbo heat shield functionality is key to unlocking enhanced engine efficiency and power output. Learn how this simple yet ingenious design choice impacts everything from fuel economy to overall vehicle dynamics.
- Understanding Turbo Heat Shield Functionality
- Impact on Intake Air Temperature: The Science Behind
- Benefits and Applications in Automotive Engineering
Understanding Turbo Heat Shield Functionality

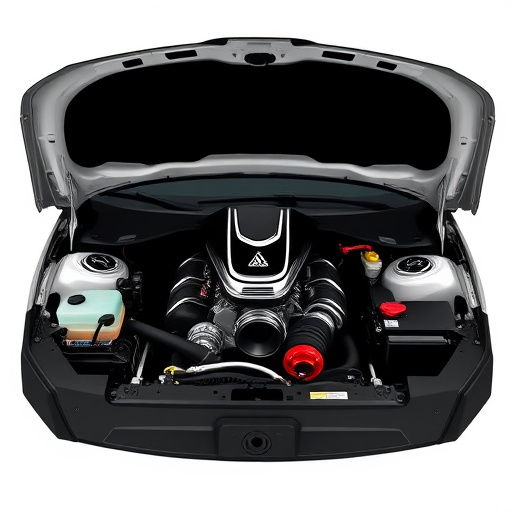
A turbo heat shield is a specialized component designed to play a crucial role in turbocharged vehicles. Its primary functionality is to insulate and protect the intake air from the intense heat generated by the turbine side of the turbocharger. This is particularly important as maintaining a cool intake air temperature (IAT) is essential for optimal engine performance and efficiency. By acting as a barrier, the heat shield ensures that the incoming air remains at a suitable temperature, allowing for better compression ratios and efficient combustion.
This component is especially valuable for those seeking high-performance parts upgrades, such as coilover kits or advanced muffler tips. In these modifications, where engine power and response are enhanced, keeping intake air cool can prevent potential performance bottlenecks. The heat shield’s role in preserving IAT ensures that the engine receives cooler, denser air, resulting in increased horsepower and torque across the entire RPM range.
Impact on Intake Air Temperature: The Science Behind

The introduction of a turbo heat shield can significantly impact intake air temperature, a crucial factor in engine performance. This component is designed to insulate and protect the turbocharger from the hot exhaust gases, preventing heat transfer into the intake system. By creating a barrier between the turbo and the hot exhaust, the heat shield reduces the chance of pre-heating the incoming air, which can otherwise lead to decreased engine efficiency.
The science behind this effect lies in the principles of thermodynamics. Intake air temperature plays a vital role in the density and pressure of the air entering the engine. When the air is heated, its density decreases, resulting in reduced air flow and potential power loss. A turbo heat shield helps maintain cooler intake air by minimizing thermal conduction from exhaust muffler tips and suspension components, ensuring that the engine receives a steady supply of dense, hot air to maximize combustion efficiency.
Benefits and Applications in Automotive Engineering

The implementation of turbo heat shields in automotive engineering brings about significant advantages for various vehicle systems. These shields are designed to protect critical intake components from the intense heat generated by turbocharged engines, a crucial aspect often overlooked in high-performance vehicles. By acting as a barrier between the hot exhaust gases and the air intake system, they prevent excessive heating of the air entering the engine, which is vital for maintaining optimal performance and efficiency.
This technology is particularly beneficial for custom car builds and performance upgrades where powerful turbocharged engines are favoured. It allows engineers to fine-tune air intake systems, ensuring a cooler, denser charge enters the combustion chamber. This, in turn, enhances the overall efficiency of the engine, resulting in improved horsepower and torque. Moreover, the strategic placement of turbo heat shields can contribute to more seamless integration of suspension kits, addressing another key area for automotive engineers seeking to enhance both performance and stability.
A turbo heat shield plays a pivotal role in automotive engineering by effectively managing heat within the engine’s intake system. By understanding its functionality and the science behind its impact on intake air temperature, engineers can leverage these benefits for enhanced performance and efficiency. This knowledge ensures that modern vehicles continue to revolutionize the industry while maintaining optimal engine health.